SeExpr QuickRef
SeExpr QuickRef
Courtesy of Walt Disney Animation Studios (See below)
Shader/XGen/Paint3d Expressions
- Variables
- Color, Masking, and Remapping Functions
- Noise Functions
- Texture Lookup Functions
- Selection Functions
- General Math Functions and Constants
- Trigonometry Functions
- Vector Functions
- Vector Support
- Curve Functions
- Misc Functions
- Operators
- Assignment Operators
- Comments
- Custom Plugins
Variables
The specific variables that are used depends on the context that the expression language is being used in. A common convention we use is to use the following variables in different contexts. These are just examples. Usually the developer of the software using expressions will register the acceptable variables with autocomplete help so that when you type $ in the expression editor a list of acceptable variables popup.
Image Variables- $u, $v -texture coords (scalars)
- $Cs, Source image color (vector)
- $As, Source image alpha (scalar)
- $Cs, Source image color (vector)
- $u, $v -texture coords (scalars)
- $P - surface point (vector). Note: $P is sampled from the Pref geometry (if available)
- $N - surface normal
- $objectId - per-surface unique object Id, typically a small integer
- $frame - current frame number
Local variables can be defined at the start of the expression:
$a = noise($P);
$b = noise($a * 1);
pow($a, 0.5) + $b
$P = $P * 10; # increase noise frequency
fbm(vnoise($P) + $P/4)
Color, Masking,and Remapping Functions
float clamp ( float x, float lo, float hi ) - constrain x to range [lo, hi]float compress ( float x, float lo, float hi )
float remap ( float x, float source, float range, float falloff, int interp )
int linear = 0
int smooth = 1
int gaussian = 2
color saturate ( color x, float amt )
color rgbtohsl ( color rgb )
color hsltorgb ( color hsl )
HSL is Hue, Saturation, Lightness (all in range [0..1] )
These functions have also been extended to support rgb and hsl values outside of the range [0..1] in a reasonable way. For any rgb or hsl value (except for negative s values), the conversion is well-defined and reversible.
float bias ( float x, float b)
float fit ( float x, float a1, float b1, float a2, float b2 )
float boxstep ( float x, float a )
float gaussstep ( float x, float a, float b )
float linearstep ( float x, float a, float b )
float smoothstep ( float x, float a, float b )
Noise Functions
float rand ( [float min, float max], [float seed] )If a seed is supplied, it will be used in addition to the internal seeds and may be used to create multiple distinct generators.
float cellnoise2 ( float x, float y )
float cellnoise3 ( float x, float y, float z )
color ccellnoise ( vector v ) - color cellnoise
float noise ( vector v )
float noise ( float x, float y )
float noise ( float x, float y, float z )
float noise ( float x, float y, float z, float w )
color cnoise ( vector v) - color noise
float snoise ( vector v) - signed noise w/ range -1 to 1.
vector vnoise (vector v ) - signed vector noise
color cnoise4 ( vector v, float t) - color noise
float snoise4 ( vector v, float t) - signed noise w/ range -1 to 1.
vector vnoise4 (vector v, float t ) - signed vector noise
float pnoise ( vector v, vector period ) - periodic noise
float perlin ( vector v )
color cperlin ( vector v) - color noise
float sperlin ( vector v) - signed noise w/ range -1 to 1.
vector vperlin (vector v ) - signed vector noise
float fbm ( vector v, int octaves = 6, float lacunarity = 2, float gain = 0.5 )
color cfbm ( vector v, int octaves = 6, float lacunarity = 2, float gain = 0.5 )
vector vfbm ( vector v, int octaves = 6, float lacunarity = 2, float gain = 0.5 )
float fbm4 ( vector v, float time, int octaves = 6, float lacunarity = 2, float gain = 0.5 )
color cfbm4 ( vector v, float time, int octaves = 6, float lacunarity = 2, float gain = 0.5 )
vector vfbm4 ( vector v, float time, int octaves = 6, float lacunarity = 2, float gain = 0.5 )
float turbulence ( vector v, int octaves = 6, float lacunarity = 2, float gain = 0.5 )
color cturbulence ( vector v, int octaves = 6, float lacunarity = 2, float gain = 0.5 )
vector vturbulence ( vector v, int octaves = 6, float lacunarity = 2, float gain = 0.5 )
float voronoi ( vector v, int type = 1, float jitter = 0.5, float fbmScale = 0, int fbmOctaves = 4, float fbmLacunarity = 2, float fbmGain = 0.5)
color cvoronoi ( vector v, int type = 1, float jitter = 0.5, float fbmScale = 0, int fbmOctaves = 4, float fbmLacunarity = 2, float fbmGain = 0.5)
vector pvoronoi ( vector v, float jitter = 0.5, float fbmScale = 0, int fbmOctaves = 4, float fbmLacunarity = 2, float fbmGain = 0.5)
Voronoi types 1 through 5:

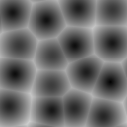
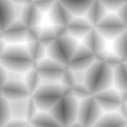
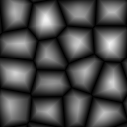
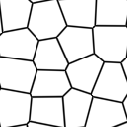
Selection Functions
int cycle ( int index, int loRange, int hiRange )int pick ( float index, int loRange, int hiRange, [float weights, ...] )
Examples:
- pick ( value, 1, 10 ) - integer values between 1 and 10 will be returned
- pick ( value, 1, 10, 2, 2.5 ) - the values 1 and 2 will be returned twice and 2.5 times as often respectively as compared to the other values (3-10)
- pick ( value, 10, 20, 1, 1, 0 ) - values 10, 11, and 13 through 20 will be returned (12 is skipped due to zero weight)
- map( 'noise.%d.map.tx', 10 ) references a file named
'noise.10.map.tx'
- map( 'fenceColor-%04d.tx', 12 ) references a file named 'fenceColor-0012.tx'
- map( 'map-%d.tx', $objectId) builds the filename based on the object Id
- map( 'map-%d.tx', cycle($objectId, 10, 20)) cycles through maps 10 through 20 based on object Id
- map( 'map-%d.tx', pick($objectId, 10, 20)) picks maps
10 through 20 randomly based on
object Id
General Math Functions and Constants
float PI= 3.14159...float E = 2.71828...
float abs ( float x) - absolute value of x
float max ( float a, float b ) - greater of a and b
float min ( float a, float b ) - lesser of a and b
float fmod ( float x, float y) - remainder of x / y (also available as '%' operator)
float cbrt ( float x ) - cube root
float sqrt ( float x ) - square root
float ceil ( float x ) - next higher integer
float floor ( float x ) - next lower integer
float round ( float x ) - nearest integer
float trunc ( float x ) - nearest integer towards zero
float exp ( float x ) - E raised to the x power
float log ( float x ) - natural logarithm
float log10 ( float x ) - base 10 logarithm
float pow ( float x, float y ) - x to the y power (also available as '^' operator)
Trigonometry Functions
float acos ( float x ) - arc cosinefloat asin ( float x ) - arc sine
float atan ( float x ) - arc tangent
float atan2 ( float y, float x) - arc tangent of y/x between -PI and PI
float cos ( float x ) - cosine
float sin ( float x ) - sine
float tan ( float x ) - tangent
float acosd ( float x ) - arc cosine in degrees
float asind ( float x ) - arc sine in degrees
float atand ( float x ) - arc tangent in degrees
float atan2d ( float y, float x ) - arc tangent in degrees of y/x between -180 and 180
float cosd ( float x ) - cosine in degrees
float sind ( float x ) - sine in degrees
float tand ( float x ) - tangent in degrees
float acosh ( float x ) - hyperbolic arc cosine
float asinh ( float x ) - hyperbolic arc sine
float atanh ( float x ) - hyperbolic arc tangent
float cosh ( float x ) - hyperbolic cosine
float sinh ( float x ) - hyperbolic sine
float tanh ( float x ) - hyperbolic tangent
float deg ( float x ) - radians to degrees
float rad ( float x ) - degrees to radians
float hypot ( float x, float y ) - length of 2d vector (x,y)
Vector Functions
float angle( vector a, vector b ) - angle between two vectors (in radians)vector cross ( vector a, vector b ) - vector cross product
float dist ( vector a, vector b ) - distance between two points
float dot ( vector a, vector b) - vector dot product
float length ( vector v ) - length of vector
vector norm ( vector v ) - vector scaled to unit length
vector ortho ( vector a, vector b ) - vector orthographic to two vectors
vector up ( vector v, vector up ) - rotates v such that the Y axis points in the given up direction
vector rotate ( vector v, vector axis, float angle ) - rotates v around axis by given angle (in radians)
Vector Support
Vectors (points, colors, or 3d vectors) may be intermixed with scalars (simple float values). If a scalar is used in a vector context, it is replicated into the three components (e.g. 0.5 becomes [0.5, 0.5, 0.5] ). If a vector is used in a scalar context, only the first component is used.One of the benefits of this is that all the functions that are defined to work with scalars automatically extend to vectors. For instance, pick, choose, cycle, spline, etc., will work just fine with vectors.
Arithmetic operators such as +, *, etc., and scalar functions are applied component-wise to vectors. For example, applying the gamma function to a map adjusts the gamma of all three color channels.
Curve Functions
Interpolation of parameter values to a set of control points is governed by the following functions.
color ccurve(float param,float pos0,color val0,int interp0,float pos1,color val1,int interp1,[...])
Interpolates color ramp given by control points at 'param'. Control points are specified
by triples of parameters pos_i, val_i, and interp_i. Interpolation codes are
0 - none, 1 - linear, 2 - smooth, 3 - spline, 4 - monotone (non-oscillating) spline
float curve(float param,float pos0,float val0,int interp0,float pos1,float val1,int interp1,[...])
Interpolates a 1D ramp defined by control points at 'param'. Control points are specified
by triples of parameters pos_i, val_i, and interp_i. Interpolation codes are
0 - none, 1 - linear, 2 - smooth, 3 - spline, 4 - monotone (non-oscillating) spline
float spline(float param,float y1,float y2,float y3,float y4,[...])
Interpolates a set of values to the parameter specified where y1, ..., yn are
distributed evenly from [0...1]
Misc Functions
void printf(string format,[param0,param1,...])
Prints a string to stdout that is formatted as given. Formatting parameters
possible are %f for float (takes first component of vector argument) or %v for
vector. For example if you wrote printf("test %f %v",[1,2,3],[4,5,6]); you
would get "test 1 [4,5,6]".
Operators (listed in decreasing precedence)
| [ a, b, c ] [ n ] |
vector constructor vector component access - n must be 0, 1, or 2 (e.g. $P[0]) |
| ^ | exponentiation (same as pow function) |
| ! | logical NOT |
| ~ | inversion (i.e. ~$A gives the same result as 1-$A) |
| * / % | multiply, divide, modulus (same as fmod function) |
| + - | add, subtract |
| < > <= >= | comparison (only uses [0] component of vectors) |
| == != | equality, inequality |
| && | logical AND |
| || | logical OR |
| ? : | conditional (like if-then-else, e.g. $u < .5 ? 0 : 1) |
| -> | apply - The function on the right of the arrow is applied to
the expression on the left. Examples: $Cs -> contrast(.7) -> clamp(0.2, 0.8) $u -> hsi(20, 1.2, 1, $Cs -> gamma(1.2)) |
Assignment Operators
Besides the basic assignment statement "$foo=$bar;" you can also do operator assignments such as "$foo+=$bar;" which is equivalent to "$foo=$foo+$bar;". Additionally there are, +=, -=, /=, %=, *=, ^=.
Comments
Any characters following a '#' to the end of the line are ignored and may be used as a comment, or for "commenting out" part of the expression. For a multi-line expression, each line may have its own comment.Custom Plugins
Custom fuctions may be written in C++ and loaded as one or more dynamic plugins. See Writing Custom Expression Plugins for more details.See Also
- Source code at GitHub
- SeExpr API Documentation
- SeExpr Language Documentation
